ECG Sensor
What they look like



An ECG is used to measure the heart’s electrical conduction system. It picks up electrical impulses generated by the polarization and depolarization of cardiac tissue and translates into a waveform. The waveform is then used to measure the rate and regularity of heartbeats, as well as the size and position of the chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart, and the effects of drugs or devices used to regulate the heart, such as a pacemaker.
Most ECGs are performed for diagnostic or research purposes on human hearts, but may also be performed on animals, usually for diagnosis of heart abnormalities or research.
Typical electroencephalogram (EEG) and electrocardiogram (ECG) sensors require conductive gel to
ensure low-impedance electrical contact between the sensor and skin, making set-up time-consuming and long-term recording problematic. But now a gel-free, non-contact EEG/ECG
sensor is used that capacitively couples to the skin.(2007 IEEE reasearch paper) and that too wearable and wirless.
Surely they have advanced in terms of usability. Earlier number of electrodes needs to be inserted within the heart in order to measure the reading. But now as it is wireless and wearable anyone can use it like any other device such as smart watch , mobile phones etc.
While a typical ECG sensor costs $40 to $50 but people are able to make it at home too under $5 provided they are low powered and less sensitive.
When it can be used



An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a recording of the electrical activity of the heart over time produced by an electrocardiograph, usually in a noninvasive recording via skin electrodes. In the US, the abbreviation "EKG", (abbreviated from the German Elektrokardiogramm).
An ECG is used to measure the heart’s electrical conduction system. It picks up electrical impulses generated by the polarization and depolarization of cardiac tissue and translates into a waveform. The waveform is then used to measure the rate and regularity of heartbeats, as well as the size and position of the chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart, and the effects of drugs or devices used to regulate the heart, such as a pacemaker.
Most ECGs are performed for diagnostic or research purposes on human hearts, but may also be performed on animals, usually for diagnosis of heart abnormalities or research.
 |
| Old ECG |
Typical electroencephalogram (EEG) and electrocardiogram (ECG) sensors require conductive gel to
ensure low-impedance electrical contact between the sensor and skin, making set-up time-consuming and long-term recording problematic. But now a gel-free, non-contact EEG/ECG
sensor is used that capacitively couples to the skin.(2007 IEEE reasearch paper) and that too wearable and wirless.
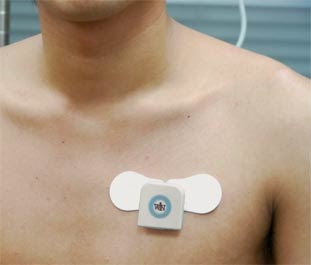 |
| WIN Human Recorder |
Surely they have advanced in terms of usability. Earlier number of electrodes needs to be inserted within the heart in order to measure the reading. But now as it is wireless and wearable anyone can use it like any other device such as smart watch , mobile phones etc.
While a typical ECG sensor costs $40 to $50 but people are able to make it at home too under $5 provided they are low powered and less sensitive.
When it can be used
- Resting EKG
- EKG after exercise
- EKG and different body positions
- EKG after using mild stimulants such as coffee or coca-cola


Comments
Post a Comment